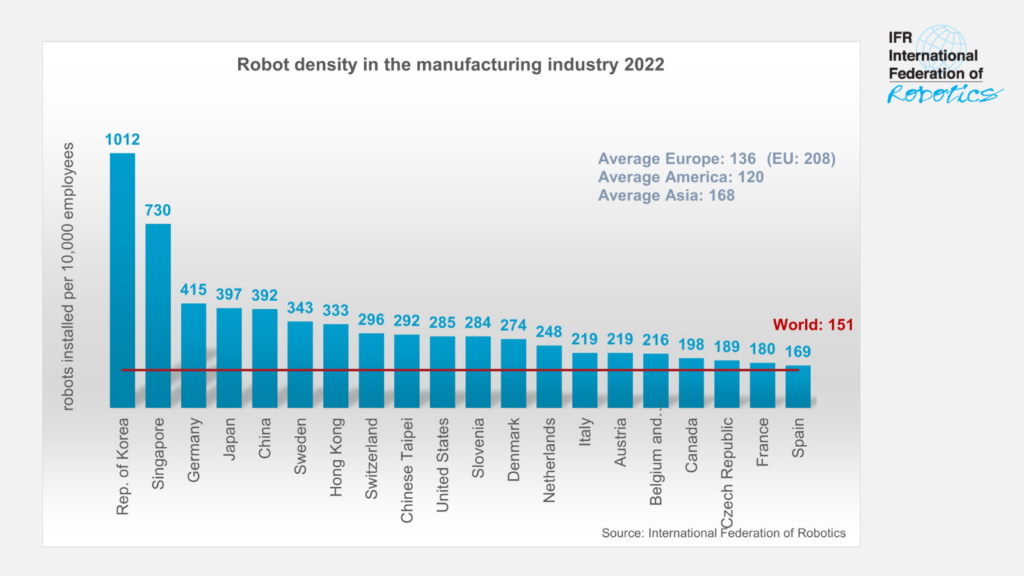
What was once considered a futuristic vision is now on the cusp of becoming industrial reality: Tesla’s humanoid robot Optimus could fundamentally change the German manufacturing landscape. With a ratio of 415 robots per 10,000 employees, Germany already occupies a leading position in Europe. The introduction of Optimus will help to finally blur the line between the vision of the future and the present.
Economic impact of Optimus
The integration of Optimus into German companies is akin to the introduction of highly developed androids in science fiction scenarios – it promises to revolutionize production processes.
The acquisition costs of Optimus are around 18,000 to 27,000 euros. The potential payback period is less than a year. Optimus therefore offers a level of efficiency that previously seemed unthinkable.
Let’s consider the following scenario:
- Optimus acquisition costs: €27,000
- Annual savings: € 32,244.00 (annual costs of a minimum wage earner incl. social security contributions)
- Amortization period: approx. 10 months
The figures shown illustrate the considerable potential for cost savings and increased efficiency. While companies should consider factors such as energy, maintenance and potential downtime costs when deciding on this technology, the return on investment remains impressive.
The biggest challenge lies in the availability and strategic integration of this technology into existing processes.
Trade union perspective and HR management
The introduction of Optimus presents companies and trade unions with new challenges.
Key issues are
- Restructuring of workplaces and areas of responsibility
- Development of further training programs for human-machine collaboration
- Fair distribution of productivity gains
- Co-determination in the integration of AI and robots
- Adaptation of occupational health and safety protocols
It is crucial that managers work proactively with trade unions and works councils to ensure smooth transitions and minimize potential conflicts.
Future-oriented skills and training
To remain competitive in this new era, companies need to invest in developing the following skills:
- Technical understanding and robot programming
- Data analysis and AI-powered decision making
- Agile project management and process optimization
- Interdisciplinary collaboration and human-machine interaction
- Continuous learning and adaptability
The dual education system in Germany represents a decisive advantage, as it enables curricula to be quickly adapted to new technological requirements as well as the practical training of skilled workers.
Competitive analysis and market positioning
The market for humanoid robots is currently going through an extremely dynamic development phase. In addition to Tesla’s Optimus, other players are positioning themselves on the market.
- Boston Dynamics (Atlas robots): Focus on mobility and balance
- Unitree (G1 robot): Cost-efficient approach for broad applications
- Figure AI (Figure 01/02): Already in use at BMW, shows potential for the automotive industry
- Agility Robotics (Digit): Specialized in logistics and warehousing
- Apptronik, Sanctuary AI, 1X Technologies: Various approaches for specific industrial applications
Companies should closely monitor developments in this area and evaluate which solutions best suit their specific requirements to make the best decision for them.
Future scenarios and strategic planning
The German automotive industry, long a flagship of the German economy, is in the midst of a profound crisis. The current situation has far-reaching effects on the entire industrial landscape and has a significant impact on possible future scenarios for the integration of robots such as Optimus.
- Gradual integration: In this scenario, there is a preference for a gradual introduction of robot technologies, especially among medium-sized companies. Given the challenges in the automotive industry, where even large companies such as Volkswagen are considering plant closures and layoffs, this cautious approach is attractive to many companies. In this way, a controlled adaptation to new technologies can be achieved while minimizing financial risks.
- Disruptive transformation: Despite the current crisis, there is an opportunity for some companies, particularly in the supplier industry, to gain a competitive advantage through the rapid and comprehensive implementation of robots. Although this entails higher risks, it may be necessary to remain competitive in the long term in the face of strong competition from Asia.
- Hybrid model: In our view, this scenario is the most likely for the German industrial landscape. For large corporations such as VW, which are already under pressure, one strategy would be to focus on rapid robot integration in certain areas while proceeding more cautiously in others. For medium-sized companies, a more gradual approach would be likely, depending on their financial situation and market position.
The choice of approach will largely depend on the specific challenges of each industry. The automotive industry, which is struggling with weak sales figures and the high cost of switching to e-mobility, may pursue a more aggressive strategy in integrating robotics technologies to reduce costs and increase efficiency.
SMEs, the backbone of the German economy, face the challenge of keeping pace with technological developments without overextending themselves financially. This is where the gradual integration of robots such as Optimus could play a decisive role in maintaining competitiveness and securing jobs at the same time.
Conclusion and outlook
The integration of Optimus and similar technologies marks a significant turning point in industrial history.
For German industry, especially SMEs, this is an opportunity to increase efficiency and innovative strength. At the same time, companies are required to implement these new technologies responsibly and sustainably.
It is fascinating to observe how the boundaries between science fiction and reality are becoming increasingly blurred. The coming years will show how companies use these technologies to adapt to changing market conditions and at the same time assume social and ethical responsibility.
In future analyses, we will look at the specific effects of these technologies on various sectors and company sizes. The focus will be on questions of human-robot interaction, changes in work processes and the long-term effects on the labor market.
The future of work in Germany will largely depend on how well the efficiency and precision of robots such as Optimus can be combined with human creativity and adaptability. It will be exciting to see how this technological revolution unfolds over the coming years.






